OSA
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep Apnea (AP-ne-ah) is a common disorder in which you have one or more pauses in breathing or shallow breaths while you sleep. Breathing pauses can last from a few seconds to minutes. They may occur 30 times or more an hour. Typically, normal breathing then starts again, sometimes with a loud snort or choking sound.
Facts
OSA in India - About 12 adults in every 100 suffer from OSA. The number includes both men and women. Children are highly at risk too.
OSA is three-fold higher in men. Probability of having OSA increases with age. Sleep Apnea usually is a chronic (ongoing) condition that disrupts your sleep. When your breathing pauses or becomes shallow, you’ll often move out of deep sleep and into light sleep.As a result, the quality of your sleep is poor, which makes you tired during the day. Sleep Apnea is a leading cause of excessive daytime sleepiness.
Overview
Sleep Apnea often goes undiagnosed. Doctors usually can't detect the condition during routine office visits. Also, no blood test can help diagnose the condition. Most people who have Sleep Apnea don't know they have it because it only occurs during sleep. A family member or bed partner might be the first to notice signs of Sleep Apnea.
The most common type of Sleep Apnea is obstructive Sleep Apnea. In this condition, the airway collapses or becomes blocked during sleep. This causes shallow breathing or breathing pauses. When you try to breathe, any air that squeezes past the blockage can cause loud snoring. Obstructive Sleep Apnea is more common in people who are overweight, but it can affect anyone. For example, small children who have enlarged tonsil tissues in their throats may have obstructive Sleep Apnea.

Causes of Sleep Apnea
When you're awake, throat muscles help keep your airway stiff and open so air can flow into your lungs. When you sleep, these muscles relax, which narrows your throat. Normally, this narrowing doesn’t prevent air from flowing into and out of your lungs. But if you have Sleep Apnea, your airway can become partially or fully blocked because:
- Your throat muscles and tongue relax more than normal.
- Your tongue and tonsils (tissue masses in the back of your mouth) are large compared with the opening into your windpipe.
- You're overweight. The extra soft fat tissue can thicken the wall of the windpipe. This narrows the inside of the windpipe, which makes it harder to keep open.
- The shape of your head and neck (bony structure) may cause a smaller airway size in the mouth and throat area.
- The aging process limits your brain signals' ability to keep your throat muscles stiff during sleep. Thus, your airway is more likely to narrow or collapse.
Not enough air flows into your lungs if your airway is partially or fully blocked during sleep. As a result, loud snoring and a drop in your blood oxygen level can occur.
If the oxygen drops to a dangerous level, it triggers your brain to disturb your sleep. This helps tighten the upper airway muscles and open your windpipe. Normal breathing then starts again, often with a loud snort or choking sound.
Frequent drops in your blood oxygen level and reduced sleep quality can trigger the release of stress hormones. These hormones raise your heart rate and increase your risk for high blood pressure, heart attack, stroke, and arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats). The hormones also can raise your risk for, or worsen, heart failure.

Who is at Risk?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea is a common condition. About half of the people who have this condition are overweight. Men are more likely than women to have Sleep Apnea. Although the condition can occur at any age, the risk increases as you get older. A family history of Sleep Apnea also increases your risk for the condition.
People who have small airways in their noses, throats, or mouths are more likely to have Sleep Apnea. Small airways might be due to the shape of these structures or allergies or other conditions that cause congestion. Small children might have enlarged tonsil tissues in their throats. Enlarged tonsil tissues raise a child’s risk for Sleep Apnea. Overweight children also might be at increased risk for Sleep Apnea.
About half of the people who have Sleep Apnea also have high blood pressure. Sleep Apnea also is linked to smoking, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, risk factors for stroke and heart failure. Race and ethnicity might play a role in the risk of developing Sleep Apnea. However, more research is needed.
Signs & Symptoms of OSA?
One of the most common signs of Obstructive Sleep Apnea is loud and chronic (ongoing) snoring. Pauses may occur in the snoring. Choking or gasping may follow the pauses. The snoring usually is loudest when you sleep on your back; it might be less noisy when you turn on your side. You might not snore every night. Over time, however, the snoring can happen more often and get louder.
You're asleep when the snoring or gasping happens. You likely won't know that you're having problems breathing or be able to judge how severe the problem is. A family member or bed partner often will notice these problems before you do.
Not everyone who snores has Sleep Apnea. Another common sign of Sleep Apnea is fighting sleepiness during the day, at work, or while driving. You may find yourself rapidly falling asleep during the quiet moments of the day when you're not active. Even if you don't have daytime sleepiness, talk with your doctor if you have problems breathing during sleep.
Other Signs and Symptoms
Others signs and symptoms of Sleep Apnea include:
- Morning headaches
- Memory or learning problems and not being able to concentrate
- Feeling irritable, depressed, or having mood swings or personality changes
- Waking up frequently to urinate
- Dry mouth or sore throat when you wake up
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness / fatigue
- Sleepiness
- Fatigue
- Lack of energy
- Irregular sleep cycle
In children, Sleep Apnea can cause hyperactivity, poor school performance, and angry or hostile behavior. Children who have Sleep Apnea also may breathe through their mouths instead of their noses during the day.
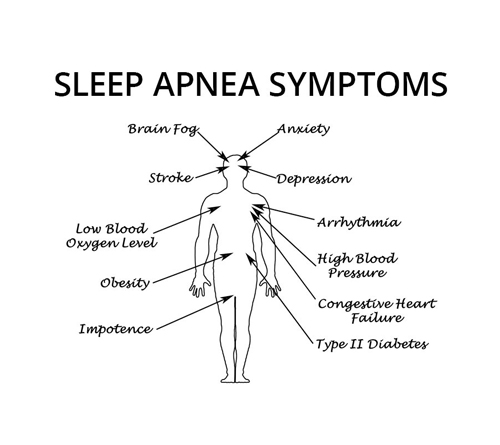
Complications of OSA
- Arterial hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- Cerebrovascular accidents (Stroke)
- Cardiovascular diseases (Irregular Heart Beats, Heart Attack, Heart Failure)
- Type 2 Diabetes (High Blood Sugar), Depression
- In children and adolescents, untreated OSA can lead to poor performance in everyday activities, at school & cause academic underachievement.
- Motor vehicle crashes.

Treatment of OSA
If Obstructive Sleep Apnea is diagnosed as “Mild”
- Weight loss
- Sleep on your side
- Take Healthy diet
- Use a different pillow
- Avoid alcohol in the evening
- Customized Exercise program
What if my OSA is diagnosed as “Moderate to Severe”?
The most successful treatment for Obstructive Sleep Apnea available today is PAP (Positive Airways Pressure) Therapy. PAP Therapy is a non-invasive non-surgical therapy that relies on 3 components:
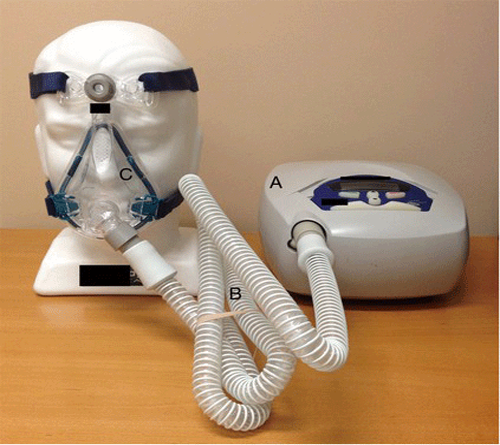
Devices mostly used in treatment process of Obstructive Sleep Apnea.

The device : this is small enough to fit on your bed side table.

The supply tubing : this connects the device and mastk.

The mask : this fits over the nose (nasal mask) or over the nose and mouth (full face mask)
The device facilitates a gentle flow of air through the upper airway. The regular airflow ensures the tongue or soft tissues near the airway don't obstruct the upper airway. By preventing collapse of the airway, PAP Therapy allows you to breathe freely through a comfortable mask, without trouble and without breaks. PAP therapy, when used as prescribed by a Sleep Doctor, reduces the symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. With regular use, over time, it could gradually normalize sleep-time breathing, and liberate you from the serious health risks associated with OSA.
Other modalities of treatments when patient is intolerant or non - compliant with CPAP
1. Oral Dental Appliances:
A specialized Dentist customizes a device to suit individual mouth types.
2. Uvulo-palato-pharyngo-plasty (UPPP)
In this operation, the Uvula and portions of the posterior soft palate, anterior and posterior Tonsillar Pillars are cut out to facilitate unobstructed air passage through the airway.
Sleep Solutions can help you...
We set up an appropriate date to do a Detailed Sleep Study in the comfort of your home.
A Technician from Sleep Solutions will arrive and set up the Sleep Data Recording Machine in the patient's room for one night. The following morning Keystone's Technician will collect the Sleep Data Recording Machine from the patients home, download the data & send it to Dr.............. for diagnosis.
Based on the data Dr. .......... will make a detailed diagnosis, and recommend a treatment customized for the patient.
Sleep Solutions will provide all help regarding the equipment, medicines and treatment right at your doorstep.
For more details feel free to Contact Us
